A team of astronomers has made a surprising discovery using the U.S. National Science Foundation Green Bank Telescope (NSF GBT): eleven fast-moving clouds of cold, neutral hydrogen gas—akin to “ice cubes”—surviving deep inside the Fermi Bubbles.
Recent News
ALMA Reveals Stunning Details of Infant Galaxies in the Early Universe
The [CII] Resolved ISM in STar-forming galaxies with ALMA (CRISTAL survey) peered back to when the Universe was only about one billion years old – a mere toddler in cosmic terms. These observations are helping scientists understand how galaxies formed and evolved from primordial gas clouds into the organized structures we see today.
NSF NRAO Leads Critical Spectrum Studies to Safeguard Radio Astronomy
The U.S. National Science Foundation National Radio Astronomy Observatory (NSF NRAO) has received funding to expand its study of an invisible—and crucial—scientific and technological resource: the radio spectrum.
Stellar Explosions and Cosmic Chemistry
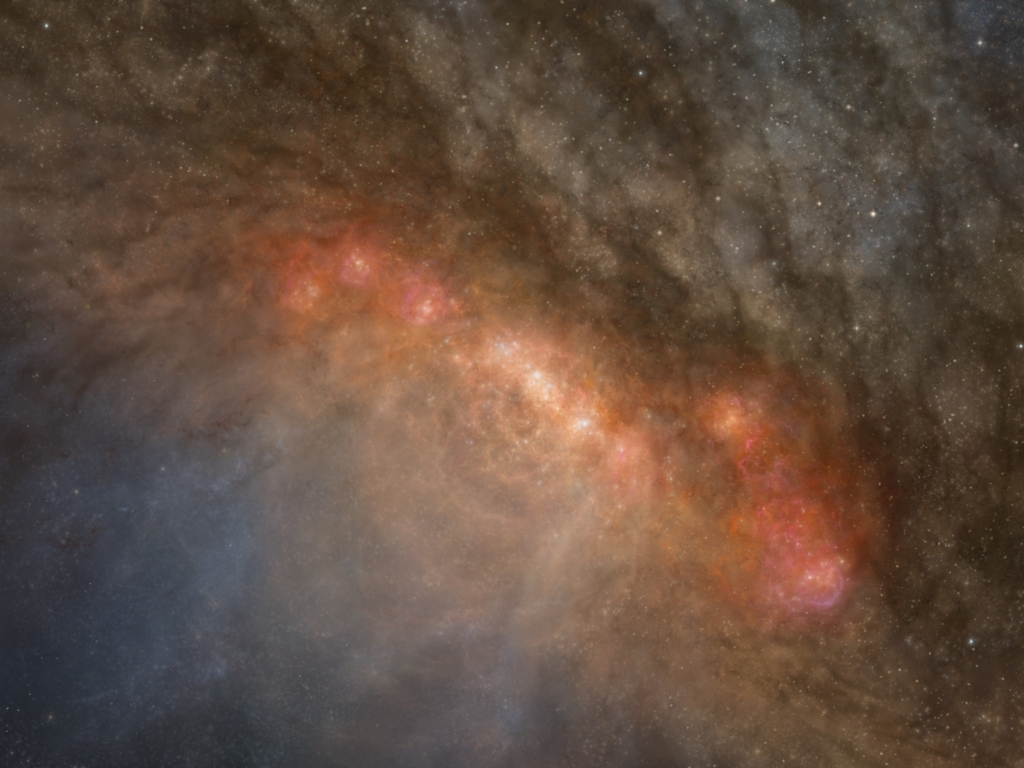

NGC 253. Credit: ALMA
Unveiling the Secrets of Starburst Galaxies with ALMA
Astronomers have discovered the secrets of a starburst galaxy producing new stars at a rate much faster than our Milk Way. This research revealed many different molecules, more than ever seen before in a galaxy like this.
This international research team used the Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array (ALMA) to observe the center of starburst galaxy NGC 253. Through ALMA’s high sensitivity and angular resolution, the team detected over one hundred molecular species in NGC 253, far more than previously observed in galaxies beyond the Milky Way.
This research was assembled from several papers from the ALMA Comprehensive High-resolution Extragalactic Molecular Inventory (ALCHEMI),a large program led by Sergio Martín of the European Southern Observatory/Joint ALMA Observatory, Nanase Harada of the National Astronomical Observatory of Japan, and Jeff Mangum of the National Radio Astronomy Observatory.
The astronomers found that the center of NGC 253 has a lot of dense gas, which helps make stars. This molecular gas is more than ten times as dense as the gas found in the center of our own Milky Way galaxy. Astronomers also discovered an abundance of complex organic molecules around regions of active star formation. When clouds of gas collide, they create shock waves that make certain molecules easier to see with telescopes like ALMA. The ALCHEMI survey expanded the molecular species atlas outside the Milky Way, doubling the number of identified species.
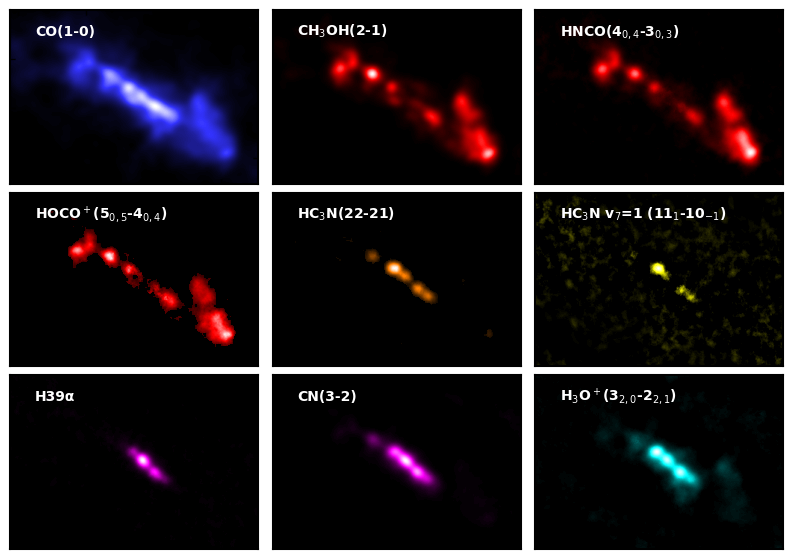
Excerpts from the ALCHEMI atlas of the center of NGC 253. The different colors represent the distribution of molecular gas (blue), shocked regions (red), relatively high-density regions (orange), young starbursts (yellow), developed starbursts (magenta), and molecular gas affected by cosmic-ray ionization (cyan). Credit: ALMA (ESO/NAOJ/NRAO), N. Harada et al.
By employing machine learning, astronomers identified molecules effectively tracing various stages of star formation. This research also observed enhanced species like H3O+ and HOC+ in developed starburst regions, indicating energy output from massive stars, which could inhibit future star formation. NGC 253 has had a lot of stars explode as supernovae, and these powerful bursts of energy make it harder for gas to come together to form new stars.
The ALCHEMI survey provided an atlas of 44 molecular species. By applying a machine-learning technique to this atlas, the researchers were able to identify which molecules are present at specific stages of star formation. Identifying tracers can help guide future ALMA observations, particularly with the anticipated wideband sensitivity upgrade. This upgrade, outlined in the ALMA 2030 Development roadmap, will allow for the simultaneous tracking of multiple tracer molecules, further advancing astronomers understanding of how stars form.
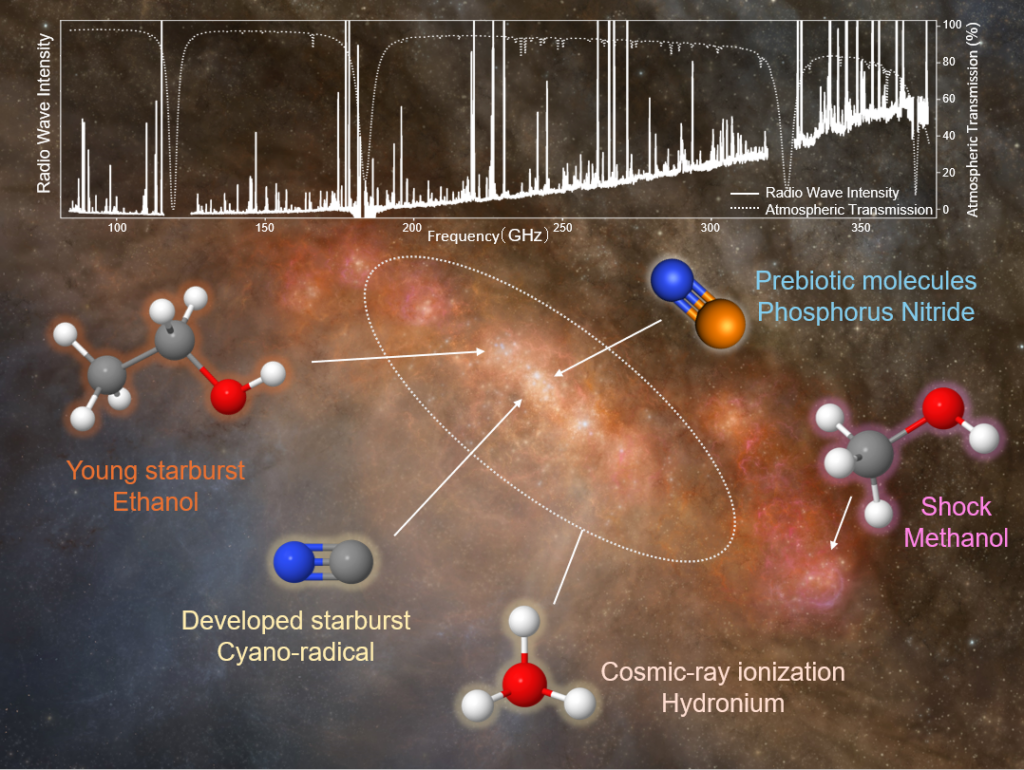
(Top) Spectra from the ALCHEMI survey. (Bottom) A schematic image of the center of the starburst galaxy, NGC 253, describing locations where various tracer molecular species are enhanced according to the ALCHEMI survey. Credit: ALMA (ESO/NAOJ/NRAO), N. Harada et al.
This news article was originally published on the NRAO website on April 1, 2024.
Recent News
Galactic Mystery: How “Ice Cubes” Survive in the Milky Way’s Blazing Bubbles
A team of astronomers has made a surprising discovery using the U.S. National Science Foundation Green Bank Telescope (NSF GBT): eleven fast-moving clouds of cold, neutral hydrogen gas—akin to “ice cubes”—surviving deep inside the Fermi Bubbles.
ALMA Reveals Stunning Details of Infant Galaxies in the Early Universe
The [CII] Resolved ISM in STar-forming galaxies with ALMA (CRISTAL survey) peered back to when the Universe was only about one billion years old – a mere toddler in cosmic terms. These observations are helping scientists understand how galaxies formed and evolved from primordial gas clouds into the organized structures we see today.
NSF NRAO Leads Critical Spectrum Studies to Safeguard Radio Astronomy
The U.S. National Science Foundation National Radio Astronomy Observatory (NSF NRAO) has received funding to expand its study of an invisible—and crucial—scientific and technological resource: the radio spectrum.
