A team of astronomers has made a surprising discovery using the U.S. National Science Foundation Green Bank Telescope (NSF GBT): eleven fast-moving clouds of cold, neutral hydrogen gas—akin to “ice cubes”—surviving deep inside the Fermi Bubbles.
Recent News
ALMA Reveals Stunning Details of Infant Galaxies in the Early Universe
The [CII] Resolved ISM in STar-forming galaxies with ALMA (CRISTAL survey) peered back to when the Universe was only about one billion years old – a mere toddler in cosmic terms. These observations are helping scientists understand how galaxies formed and evolved from primordial gas clouds into the organized structures we see today.
NSF NRAO Leads Critical Spectrum Studies to Safeguard Radio Astronomy
The U.S. National Science Foundation National Radio Astronomy Observatory (NSF NRAO) has received funding to expand its study of an invisible—and crucial—scientific and technological resource: the radio spectrum.
Spotted: ‘Death Star’ Black Holes in Action
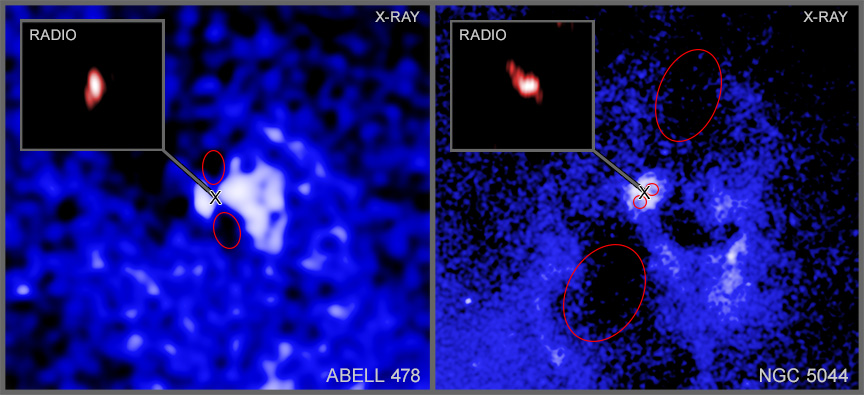
Huge black holes are firing powerful beams of particles into space — and then changing their aim to fire at new targets. This discovery, made using NASA’s Chandra X-ray Observatory and the U.S. National Science Foundation (NSF) National Radio Astronomy Observatory’s (NRAO) Very Long Baseline Array (VLBA), shows what kind of widespread impact black holes can have on their surrounding galaxy and beyond.
A team of astronomers looked at 16 supermassive black holes in galaxies surrounded by hot gas detected in X-rays by Chandra. Using radio data from the VLBA, operated by the National Radio Astronomy Observatory, they studied the directions of beams — also known as jets — of particles fired a few light-years away from the black holes. This gives the scientists a picture of where each beam is currently pointed, as seen from Earth. Each black hole fires two beams in opposite directions.
The team then used Chandra data to study pairs of cavities, or bubbles, in the hot gas that were created in the past by the beams pushing gas outwards. The locations of large outer cavities indicate the direction those beams pointed millions of years earlier. The researchers then compared the directions of the radio beams with the directions of the pairs of cavities. Read the full release.
This news article was originally published on the NRAO website on May 22, 2024.
Recent News
Galactic Mystery: How “Ice Cubes” Survive in the Milky Way’s Blazing Bubbles
A team of astronomers has made a surprising discovery using the U.S. National Science Foundation Green Bank Telescope (NSF GBT): eleven fast-moving clouds of cold, neutral hydrogen gas—akin to “ice cubes”—surviving deep inside the Fermi Bubbles.
ALMA Reveals Stunning Details of Infant Galaxies in the Early Universe
The [CII] Resolved ISM in STar-forming galaxies with ALMA (CRISTAL survey) peered back to when the Universe was only about one billion years old – a mere toddler in cosmic terms. These observations are helping scientists understand how galaxies formed and evolved from primordial gas clouds into the organized structures we see today.
NSF NRAO Leads Critical Spectrum Studies to Safeguard Radio Astronomy
The U.S. National Science Foundation National Radio Astronomy Observatory (NSF NRAO) has received funding to expand its study of an invisible—and crucial—scientific and technological resource: the radio spectrum.
