2025 was an incredibly productive year for AUI, marked by significant advances across astronomy, energy, advanced therapeutics, and STEM education and workforce development.
Recent News
ALMA Reveals Teenage Years of New Worlds
The ALMA survey to Resolve exoKuiper belt Substructures (ARKS), using the Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array (ALMA), has produced the sharpest images ever of 24 debris disks, the dusty belts left after planets finish forming. These disks are the cosmic equivalent of the teenage years for planetary systems—somewhat more mature than newborn, planet-forming disks, but not yet settled into adulthood.
The NSF Very Large Array Helps Reveal Record-Breaking Stream of Super-Heated Gas from Nearby Galaxy
New radio images from the the U.S. National Science Foundation Very Large Array trace a pair of powerful plasma jets launched by galaxy VV 340a’s central supermassive black hole, which appear to be driving hot coronal gas out of the galaxy and shutting down future star formation.
Spotted: ‘Death Star’ Black Holes in Action
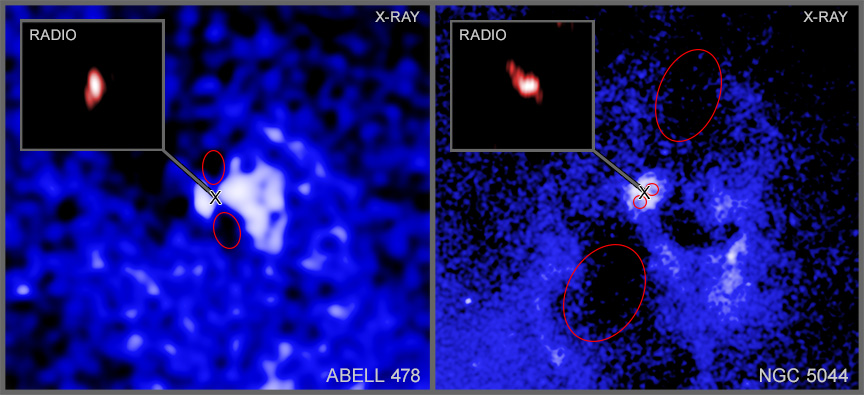
Huge black holes are firing powerful beams of particles into space — and then changing their aim to fire at new targets. This discovery, made using NASA’s Chandra X-ray Observatory and the U.S. National Science Foundation (NSF) National Radio Astronomy Observatory’s (NRAO) Very Long Baseline Array (VLBA), shows what kind of widespread impact black holes can have on their surrounding galaxy and beyond.
A team of astronomers looked at 16 supermassive black holes in galaxies surrounded by hot gas detected in X-rays by Chandra. Using radio data from the VLBA, operated by the National Radio Astronomy Observatory, they studied the directions of beams — also known as jets — of particles fired a few light-years away from the black holes. This gives the scientists a picture of where each beam is currently pointed, as seen from Earth. Each black hole fires two beams in opposite directions.
The team then used Chandra data to study pairs of cavities, or bubbles, in the hot gas that were created in the past by the beams pushing gas outwards. The locations of large outer cavities indicate the direction those beams pointed millions of years earlier. The researchers then compared the directions of the radio beams with the directions of the pairs of cavities. Read the full release.
This news article was originally published on the NRAO website on May 22, 2024.
Recent News
Making Scientific Breakthroughs Possible in 2025
2025 was an incredibly productive year for AUI, marked by significant advances across astronomy, energy, advanced therapeutics, and STEM education and workforce development.
ALMA Reveals Teenage Years of New Worlds
The ALMA survey to Resolve exoKuiper belt Substructures (ARKS), using the Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array (ALMA), has produced the sharpest images ever of 24 debris disks, the dusty belts left after planets finish forming. These disks are the cosmic equivalent of the teenage years for planetary systems—somewhat more mature than newborn, planet-forming disks, but not yet settled into adulthood.
The NSF Very Large Array Helps Reveal Record-Breaking Stream of Super-Heated Gas from Nearby Galaxy
New radio images from the the U.S. National Science Foundation Very Large Array trace a pair of powerful plasma jets launched by galaxy VV 340a’s central supermassive black hole, which appear to be driving hot coronal gas out of the galaxy and shutting down future star formation.
