Researchers have identified an exceptionally unusual cosmic object known as a Long Period Radio Transient (LPT), named CHIME J1634+44.
Recent News
Astronomers Discover Massive Molecular Cloud Hidden in Milky Way
In a new study published in the Astrophysical Journal, researchers using the U.S. National Science Foundation Green Bank Telescope (NSF GBT) have peered into a molecular cloud known as M4.7-0.8, nicknamed the Midpoint cloud. Their observations have revealed a dynamic region bustling with activity, including potential sites of new star formation.
Galactic Mystery: How “Ice Cubes” Survive in the Milky Way’s Blazing Bubbles
A team of astronomers has made a surprising discovery using the U.S. National Science Foundation Green Bank Telescope (NSF GBT): eleven fast-moving clouds of cold, neutral hydrogen gas—akin to “ice cubes”—surviving deep inside the Fermi Bubbles.
Radio Observations of Compact Symmetric Objects Shed New Light on Black Hole Phenomenon
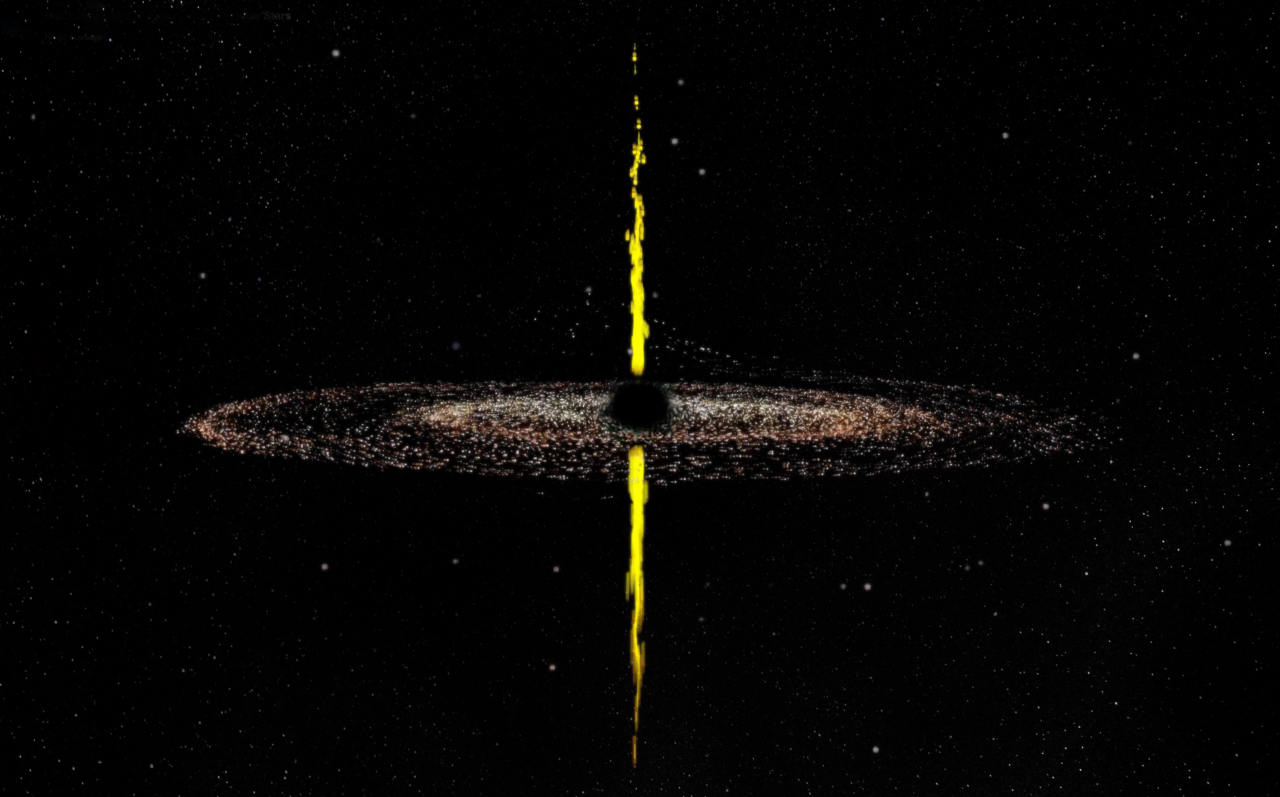

Credit: S. Dagnello, B. Saxton/NRAO/AUI/NSF
A groundbreaking investigation into Compact Symmetric Objects (CSOs), a peculiar class of galaxies, has revealed new insights into their spectacular but short-lived existence
Compact Symmetric Objects (CSOs) have long puzzled astronomers with their unique characteristics. These active galaxies harbor supermassive black holes that emit powerful jets traveling at near-light speeds in opposite directions. However, unlike their counterparts in other galaxies, these jets remain compact, not extending out to great distances as expected. For decades, scientists presumed that CSOs were youthful entities, with their jets destined to expand over time.
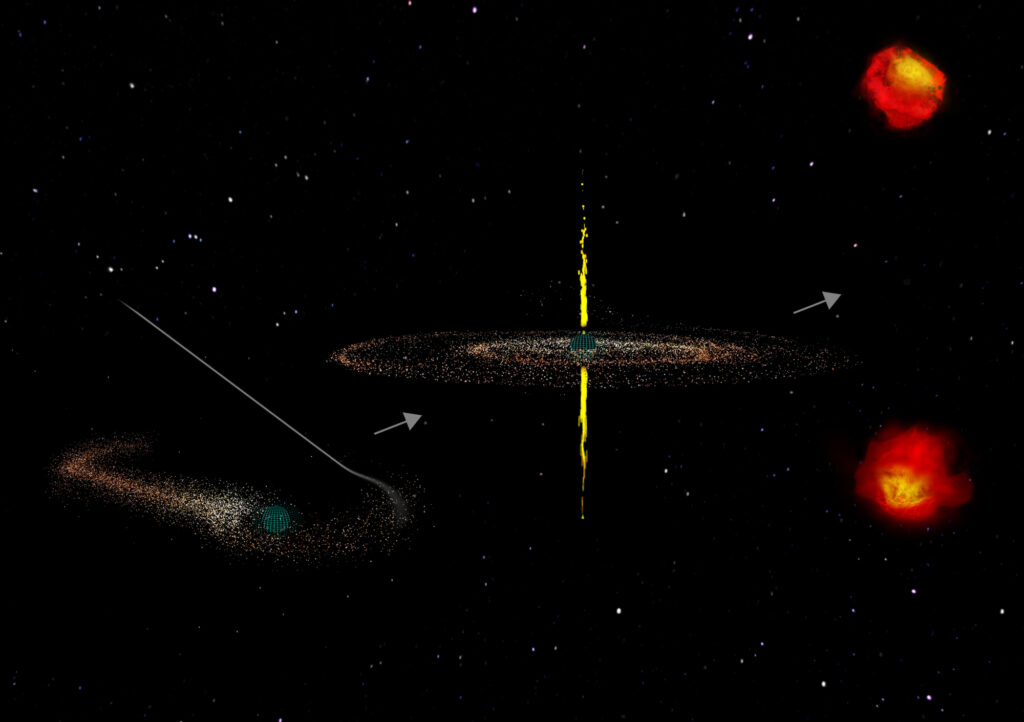
When a star is captured by the gravitational force of a black hole and shredded, or spaghettified, sometimes twin jets spiral outward. These jets can give birth to Compact Symmetrical Objects (CSOs), which scientists have confirmed are a unique class of active galaxies.
New findings, published in three papers in The Astrophysical Journal, challenge this notion. The Caltech-led team, spearheaded by Anthony (Tony) Readhead, Robinson Professor of Astronomy, Emeritus, discovered that CSOs have relatively short lifespans. Through an exhaustive review of literature and observations, the team identified over 3,000 CSO candidates, confirming 64 as authentic CSOs and recognizing 15 new candidates. These objects were previously observed by the U.S. National Science Foundation National Radio Astronomy Observatory (NSF NRAO)’s Very Long Baseline Array (VLBA), renowned for its unparalleled resolution.
The studies, funded by NSF, NASA, Caltech, and the Max Planck Institute for Radio Astronomy in Bonn, Germany, mark a significant step forward in understanding the dynamic processes shaping our universe. Read the full Caltech release and view NRAO’s scientific visualization animation.
About NRAO
The National Radio Astronomy Observatory (NRAO) is a facility of the U.S. National Science Foundation, operated under cooperative agreement by Associated Universities, Inc.
For media inquiries or further information, please contact:
NRAO Media Contact
Corrina C. Jaramillo Feldman
Public Information Officer – New Mexico
VLA, VLBA, ngVLA
Tel: +1 505-366-7267
[email protected]
This news article was originally published on the NRAO website on March 26, 2024.
Recent News
Space’s Spinning Enigma: A ‘Unicorn’ Object Defies Astrophysics
Researchers have identified an exceptionally unusual cosmic object known as a Long Period Radio Transient (LPT), named CHIME J1634+44.
Astronomers Discover Massive Molecular Cloud Hidden in Milky Way
In a new study published in the Astrophysical Journal, researchers using the U.S. National Science Foundation Green Bank Telescope (NSF GBT) have peered into a molecular cloud known as M4.7-0.8, nicknamed the Midpoint cloud. Their observations have revealed a dynamic region bustling with activity, including potential sites of new star formation.
Galactic Mystery: How “Ice Cubes” Survive in the Milky Way’s Blazing Bubbles
A team of astronomers has made a surprising discovery using the U.S. National Science Foundation Green Bank Telescope (NSF GBT): eleven fast-moving clouds of cold, neutral hydrogen gas—akin to “ice cubes”—surviving deep inside the Fermi Bubbles.
