A small cohort of educators, scientists and environmental leaders will embark March 3-14 to the southern edge of the world for Mission Patagonia, an immersive outdoor environmental education experience designed to foster deep connection to place, people and planet.
Recent News
AARO Releases Report on Unidentified Anomalous Phenomena (UAP)
The U.S. Department of Defense recently released 2025 UAP Workshop: Narrative Data, Infrastructures, and Analysis. The report details key findings from the workshop conducted at AUI headquarters in August of 2025.
OCEAN Kids ‘Nurdle Patrol’ Engages Students and Builds Environmental Knowledge
“OCEAN Kids: Nurdle Patrol” empowers children to fight plastic pollution by enrolling them in a playful, audio-led “Secret Agent” mission.
Groundbreaking Magnetic Field Discovery Near Massive Protostar
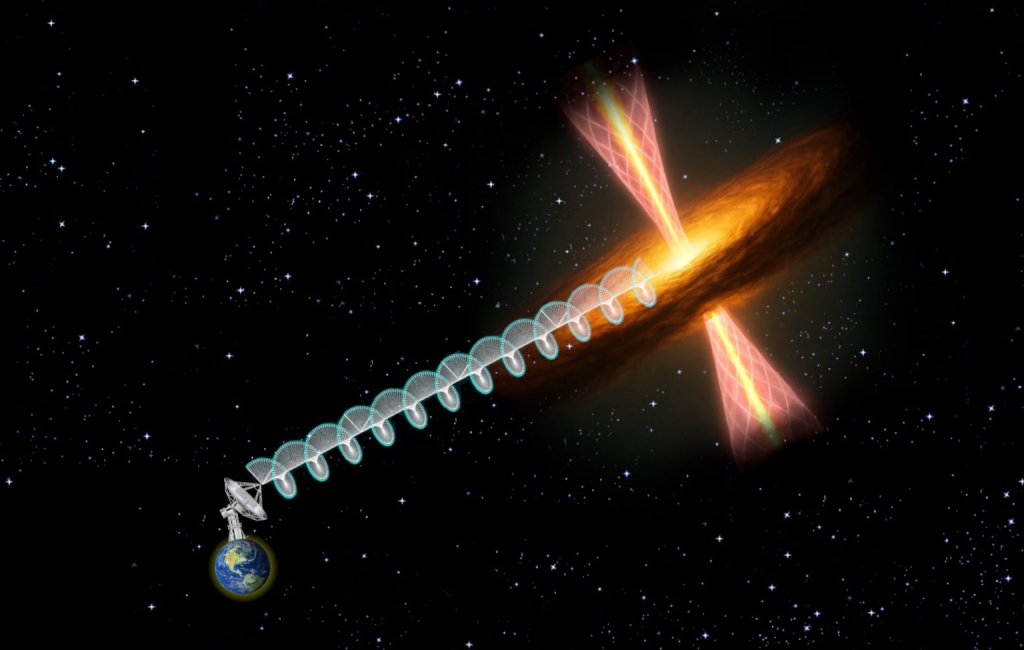
The U.S. National Science Foundation National Radio Astronomy Observatory (NSF NRAO) proudly announces a major breakthrough in our understanding of star formation, thanks to the unparalleled capabilities of the U.S. National Science Foundation Karl G. Jansky Very Large Array (NSF VLA). An international team, led by astronomers from the Indian Institute of Space Science and Technology (IIST) and the Indian Institute of Science (IISc), has for the first time detected circular polarization in radio emission originating from a massive protostar, IRAS 18162-2048—unveiling fresh clues about the cosmic forces shaping our universe.
Circularly polarized radio waves have been directly observed from a young, massive protostar, a phenomenon previously recorded only near black holes and low-mass protostars, demonstrating a new link between diverse cosmic environments. This rare signal, detected using the NSF VLA, has enabled astronomers to infer magnetic field strengths of about 20–35 Gauss close to the forming star. These values are roughly 100 times stronger than Earth’s magnetic field—providing the first direct clues to magnetic field strengths in such extreme environments. The findings reinforce a long-standing theory that the mechanisms launching powerful astrophysical jets are fundamentally similar, from low-mass stars through to supermassive black holes.
NSF NRAO is honored to contribute this critical technology and support to discoveries that deepen humanity’s knowledge of the cosmos. Read the full releases from IIST and IISc.
About NRAO
The National Radio Astronomy Observatory (NRAO) is a facility of the U.S. National Science Foundation, operated under cooperative agreement by Associated Universities, Inc.
This news article was originally published on the NRAO website on July 18, 2025.
Recent News
Mission Patagonia Welcomes Its 2026 Nature Guardians
A small cohort of educators, scientists and environmental leaders will embark March 3-14 to the southern edge of the world for Mission Patagonia, an immersive outdoor environmental education experience designed to foster deep connection to place, people and planet.
AARO Releases Report on Unidentified Anomalous Phenomena (UAP)
The U.S. Department of Defense recently released 2025 UAP Workshop: Narrative Data, Infrastructures, and Analysis. The report details key findings from the workshop conducted at AUI headquarters in August of 2025.
OCEAN Kids ‘Nurdle Patrol’ Engages Students and Builds Environmental Knowledge
“OCEAN Kids: Nurdle Patrol” empowers children to fight plastic pollution by enrolling them in a playful, audio-led “Secret Agent” mission.
