New radio images from the the U.S. National Science Foundation Very Large Array trace a pair of powerful plasma jets launched by galaxy VV 340a’s central supermassive black hole, which appear to be driving hot coronal gas out of the galaxy and shutting down future star formation.
Recent News
Radio Telescopes Uncover ‘Invisible’ Gas Around Record-Shattering Cosmic Explosion
Astronomers using the U.S. National Science Foundation Very Large Array and the Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array have revealed a dense cocoon of gas around one of the most extreme cosmic explosions ever seen, showing that a ravenous black hole ripped apart a massive star and then lit up its surroundings with powerful X-rays.
New Discovery Challenges Evolution of Galaxy Clusters
Peering back in time, around 12 billion years, astronomers using the Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array (ALMA) have found the most distant and direct evidence of scorching gas in a forming galaxy cluster, SPT2349-56. The hot plasma, seen when the Universe was just 1.4 billion years old, is far hotter and more pressurized than current theories predicted for such an early system.
Successful Test Paves Way for New Planetary Radar
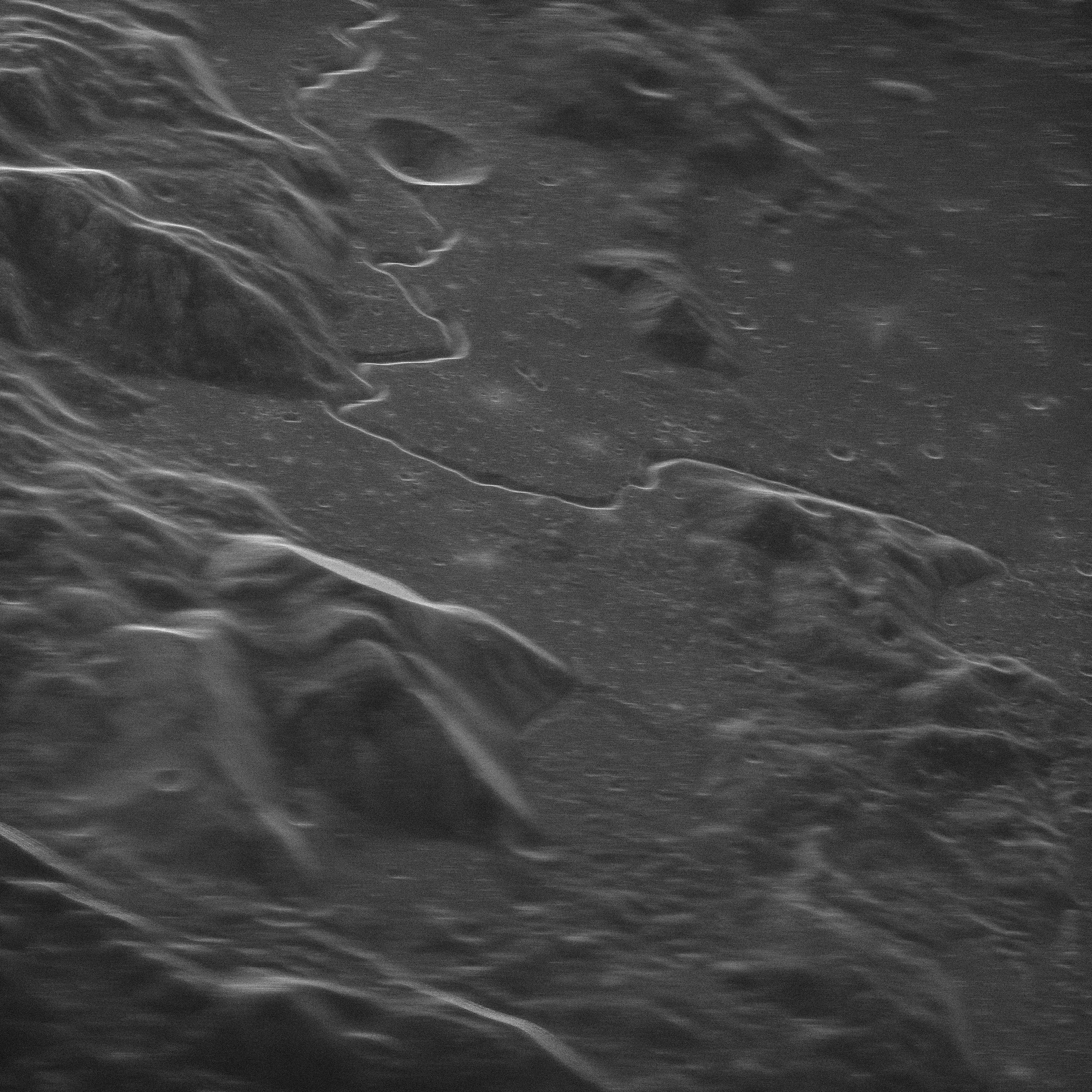
The National Science Foundation’s Green Bank Observatory (GBO) and National Radio Astronomy Observatory (NRAO), and Raytheon Intelligence & Space conducted a test in November to prove that a new radio telescope system can capture high-resolution images in near-Earth space.
GBO’s Green Bank Telescope (GBT) in West Virginia — the world’s largest fully steerable radio telescope — was outfitted with a new transmitter developed by Raytheon Intelligence & Space, allowing it to transmit a radar signal into space. The NRAO’s continent-wide Very Long Baseline Array (VLBA) received the reflected signal and produced images of the Apollo 15 moon landing site.
The proof-of-concept test, culminating a two-year effort, paves the way for designing a more powerful transmitter for the telescope. More power will allow enhanced detection and imaging of small objects passing by the Earth, moons orbiting around other planets and other debris in the Solar System.
The technology was developed as part of a cooperative research and development agreement between NRAO, GBO, and Raytheon.
“This project opens a whole new range of capabilities for both NRAO and GBO,” said Tony Beasley, director of the National Radio Astronomy Observatory and vice president for Radio Astronomy at Associated Universities, Inc. (AUI). “We’ve participated before in important radar studies of the Solar System, but turning the GBT into a steerable planetary radar transmitter will greatly expand our ability to pursue intriguing new lines of research.”
Using the information collected with this latest test, the participants will finalize a plan to develop a 500-kilowatt, high-power radar system that can image objects in the Solar System with unprecedented detail and sensitivity. The increased performance also will allow astronomers to use radar signals as far away as the orbits of Uranus and Neptune, increasing our understanding of the Solar System.
“The planned system will be a leap forward in radar science, allowing access to never before seen features of the Solar System from right here on Earth,” said Karen O’Neil, the Green Bank Observatory site director.
“Raytheon’s radar techniques could ultimately improve our ability to explore the Solar System,” said Steven Wilkinson, Principal Engineering Fellow at Raytheon Intelligence & Space. “Working with the astronomy community allows us to apply decades of radar know-how to a project that provides high-resolution images of near-Earth objects.”
“We are excited to be partnering with Raytheon and applying their radar expertise to transform our observatories’ telescopes in new science areas,” said AUI President Adam Cohen.
The National Radio Astronomy Observatory and the Green Bank Observatory are facilities of the National Science Foundation, operated under cooperative agreement by Associated Universities, Inc.
This news article was originally published on the NRAO website on January 28, 2021.
Recent News
The NSF Very Large Array Helps Reveal Record-Breaking Stream of Super-Heated Gas from Nearby Galaxy
New radio images from the the U.S. National Science Foundation Very Large Array trace a pair of powerful plasma jets launched by galaxy VV 340a’s central supermassive black hole, which appear to be driving hot coronal gas out of the galaxy and shutting down future star formation.
Radio Telescopes Uncover ‘Invisible’ Gas Around Record-Shattering Cosmic Explosion
Astronomers using the U.S. National Science Foundation Very Large Array and the Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array have revealed a dense cocoon of gas around one of the most extreme cosmic explosions ever seen, showing that a ravenous black hole ripped apart a massive star and then lit up its surroundings with powerful X-rays.
New Discovery Challenges Evolution of Galaxy Clusters
Peering back in time, around 12 billion years, astronomers using the Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array (ALMA) have found the most distant and direct evidence of scorching gas in a forming galaxy cluster, SPT2349-56. The hot plasma, seen when the Universe was just 1.4 billion years old, is far hotter and more pressurized than current theories predicted for such an early system.
