The ALMA survey to Resolve exoKuiper belt Substructures (ARKS), using the Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array (ALMA), has produced the sharpest images ever of 24 debris disks, the dusty belts left after planets finish forming. These disks are the cosmic equivalent of the teenage years for planetary systems—somewhat more mature than newborn, planet-forming disks, but not yet settled into adulthood.
Recent News
The NSF Very Large Array Helps Reveal Record-Breaking Stream of Super-Heated Gas from Nearby Galaxy
New radio images from the the U.S. National Science Foundation Very Large Array trace a pair of powerful plasma jets launched by galaxy VV 340a’s central supermassive black hole, which appear to be driving hot coronal gas out of the galaxy and shutting down future star formation.
Radio Telescopes Uncover ‘Invisible’ Gas Around Record-Shattering Cosmic Explosion
Astronomers using the U.S. National Science Foundation Very Large Array and the Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array have revealed a dense cocoon of gas around one of the most extreme cosmic explosions ever seen, showing that a ravenous black hole ripped apart a massive star and then lit up its surroundings with powerful X-rays.
Space Company Taps Coast-to-Coast Radio Telescopes for Moon Mission
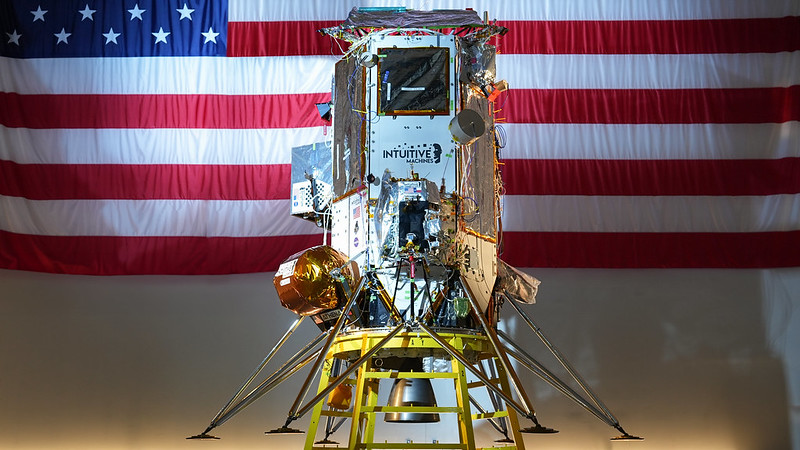
Intuitive Machines partners with NSF National Radio Astronomy Observatory, using 10 iconic U.S. telescopes from Hawaii to Virgin Islands to guide Nova-C lunar lander’s mission
The U.S. National Science Foundation National Radio Astronomy Observatory (NSF NRAO) is supporting Intuitive Machines’ second lunar mission, IM-2, which landed on the surface of the Moon, Thursday, March 6th.
Intuitive Machines has been working with the NSF NRAO over the past year to utilize the NSF Very Long Baseline Array (NSF VLBA) to support precise tracking and data downlink of Intuitive Machines’ Nova-C lunar lander, named Athena, during its mission to the Moon.
“The NRAO adds significant capability to Intuitive Machines’ Lunar Data Network,” said Intuitive Machines CEO Steve Altemus. “Using multiple, strategically located, world-class radio telescopes and ground stations enables our mission controllers to precisely track Athena through near-continuous, data-driven communications.”
The NSF NRAO will provide Intuitive Machines with access to its NSF VLBA network of radio telescopes, in ten locations across the United States, to receive data transmitted by the Nova-C lander during its journey to the Moon, while in lunar orbit, and after landing. The NSF GBT, the world’s largest fully steerable radio telescope, will also collect data. This mission support will improve the accuracy of the lander’s orbit determination through real-time or near-real-time position data.
“NRAO is excited to support Intuitive Machines in their second groundbreaking lunar mission,” said NSF NRAO assistant director Joe McMullin, who managed this project. “Our telescopes and expertise in radio astronomy will contribute to this mission’s success by providing accurate positional data and reliable communication links. NRAO recognizes the value in supporting commercial partnerships to advance space exploration and scientific discovery.”
About NRAO
The National Radio Astronomy Observatory (NRAO) is a facility of the National Science Foundation, operated under cooperative agreement by Associated Universities, Inc. NRAO designs, builds, and operates cutting-edge radio telescopes for use by scientists around the world.
This news article was originally published on the NRAO website on March 6, 2025.
Recent News
ALMA Reveals Teenage Years of New Worlds
The ALMA survey to Resolve exoKuiper belt Substructures (ARKS), using the Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array (ALMA), has produced the sharpest images ever of 24 debris disks, the dusty belts left after planets finish forming. These disks are the cosmic equivalent of the teenage years for planetary systems—somewhat more mature than newborn, planet-forming disks, but not yet settled into adulthood.
The NSF Very Large Array Helps Reveal Record-Breaking Stream of Super-Heated Gas from Nearby Galaxy
New radio images from the the U.S. National Science Foundation Very Large Array trace a pair of powerful plasma jets launched by galaxy VV 340a’s central supermassive black hole, which appear to be driving hot coronal gas out of the galaxy and shutting down future star formation.
Radio Telescopes Uncover ‘Invisible’ Gas Around Record-Shattering Cosmic Explosion
Astronomers using the U.S. National Science Foundation Very Large Array and the Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array have revealed a dense cocoon of gas around one of the most extreme cosmic explosions ever seen, showing that a ravenous black hole ripped apart a massive star and then lit up its surroundings with powerful X-rays.
