A new study connects the black hole’s famous ring of light to a compact region that marks the likely base of the jet, bringing scientists closer to understanding how black holes power some of the brightest beacons in the universe.
Recent News
Magnetic Superhighways Discovered in a Starburst Galaxy’s Winds
Using the Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array (ALMA), an international team of astronomers has mapped a magnetic highway driving a powerful galactic wind into the nearby galaxy merger of Arp 220, revealing for the first time that its fast, molecular outflows are strongly magnetized and likely helping to drive metals, dust, and cosmic rays into the space around the galaxy.
Making Scientific Breakthroughs Possible in 2025
2025 was an incredibly productive year for AUI, marked by significant advances across astronomy, energy, advanced therapeutics, and STEM education and workforce development.
Telescopes Show the Milky Way’s Black Hole is Ready for a Kick
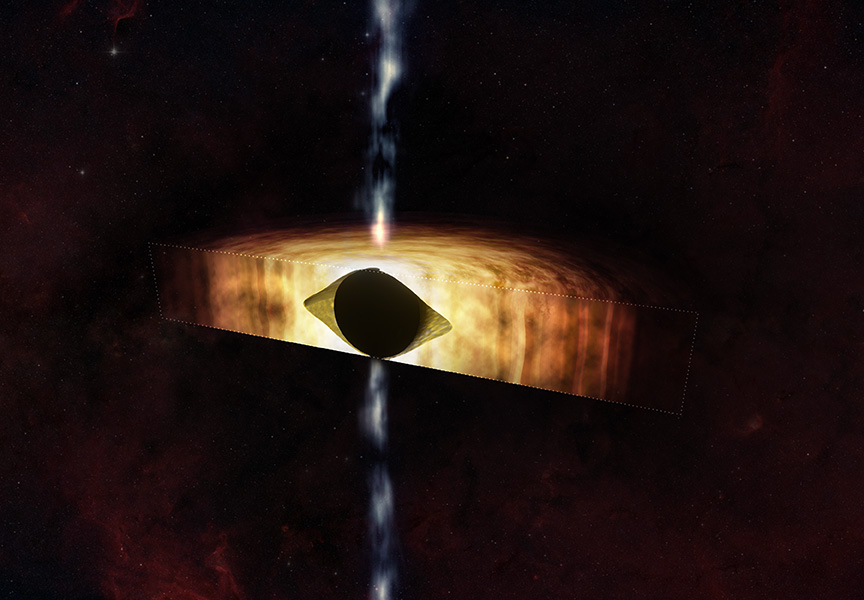
Credit: NASA/CXC/M. Weiss
Putting a new spin on the Milky Way’s black hole
The supermassive black hole in the center of the Milky Way is spinning so quickly it is warping the spacetime surrounding it into a shape that can look like a football, according to a new study using data from NASA’s Chandra X-ray Observatory and the National Science Foundation’s Karl G. Jansky Very Large Array (VLA).
Astronomers call this giant black hole Sagittarius A* (Sgr A* for short), which is located about 26,000 light-years away from Earth in the center of our galaxy.
Black holes have two fundamental properties: their mass (how much they weigh) and their spin (how quickly they rotate). Determining either of these two values tells scientists a great deal about any black hole and how it behaves.
A team of astronomers have unveiled a new method for determining the rotational speed of the enigmatic black hole, Sgr A*. By combining X-ray and radio data, the team observed the movement of surrounding material and deduced the angular velocity of Sgr A*. Astonishingly, their findings revealed that Sgr A* spins at a rate reaching approximately 60% of the maximum possible value. This boundary is determined by the fundamental constraint that nothing can travel faster than the speed of light. The team’s discovery challenges previous estimates made by astronomers, which spanned from Sgr A* being stationary to rotating at nearly the fastest rate conceivable. This groundbreaking research sheds new light on the dynamic nature of black holes and opens up exciting avenues for further exploration into their mysteries.
The paper describing these results led by Ruth Daly is published in the January 2024 issue of the Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society and appears online.
“Our work may help settle the question of how fast our galaxy’s supermassive black hole is spinning,” said Ruth Daly of Penn State University, who is the lead author on the new study. “Our results indicate that Sgr A* is spinning very rapidly, which is interesting and has far reaching implications..” This release was originally shared by NASA’s Chandra X-ray Observatory. Read the full release.
About Chandra
NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center manages the Chandra program. The Smithsonian Astrophysical Observatory’s Chandra X-ray Center controls science operations from Cambridge, Massachusetts, and flight operations from Burlington, Massachusetts.
About NRAO
The National Radio Astronomy Observatory (NRAO) is a facility of the National Science Foundation, operated under a cooperative agreement by Associated Universities, Inc.
NRAO Media Contact
Corrina C. Jaramillo Feldman
Public Information Officer – New Mexico
VLA, VLBA, ngVLA
Tel: +1 505-366-7267
[email protected]
This news article was originally published on the NRAO website on February 8, 2024.
Recent News
New Event Horizon Telescope Results Trace M87 Jet Back to Its Black Hole
A new study connects the black hole’s famous ring of light to a compact region that marks the likely base of the jet, bringing scientists closer to understanding how black holes power some of the brightest beacons in the universe.
Magnetic Superhighways Discovered in a Starburst Galaxy’s Winds
Using the Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array (ALMA), an international team of astronomers has mapped a magnetic highway driving a powerful galactic wind into the nearby galaxy merger of Arp 220, revealing for the first time that its fast, molecular outflows are strongly magnetized and likely helping to drive metals, dust, and cosmic rays into the space around the galaxy.
Making Scientific Breakthroughs Possible in 2025
2025 was an incredibly productive year for AUI, marked by significant advances across astronomy, energy, advanced therapeutics, and STEM education and workforce development.
